Ergonomics, Workflow and Design
Esaote has started some years ago a review of its approach to the topics of Ergonomics, Workflow and Design in Diagnostic Ultrasound.
Clinical Need
The ergonomics of ultrasound systems are mentioned in several guidelines from regulatory organizations and healthcare institutions. Almost 80% of sonographers report pain or discomfort within 5 years of entering the profession. Common areas affected by this issue are the neck, shoulders, wrists, hands, back, and eyes.
Clinical evaluation
A multidisciplinary approach is needed to ensure that systems and probes are designed ergonomically. Ultrasound system ergonomics and design is complex, involving many aspects such as:
- The technical and clinical experience of users
- The routine and personal attitude of users
- Clinical application, with different procedures and patients
- Clinical workflow, which varies according to the institution and department
Measurements and evaluations are required to design the system and accessories. Considering all the different outputs, technologies are needed to assess biomechanical and cognitive factors such as:
- Motion analysis, where optoelectronic cameras are used to follow user movements while performing real clinical protocols, in order to evaluate possible workflows and system designs.
- Eye tracking analyses user attention to focal areas, revealing which controls are more natural.
- Superficial electromyography measures the muscle activity of users while operating the system and the probe. Wireless sensors are used, allowing the user to move freely throughout clinical tests.
- Digital human modelling is used to test design ideas at an early stage in CAD (Computer Aided Design).

Digital human modelling and motion analysis
Clinical Benefits
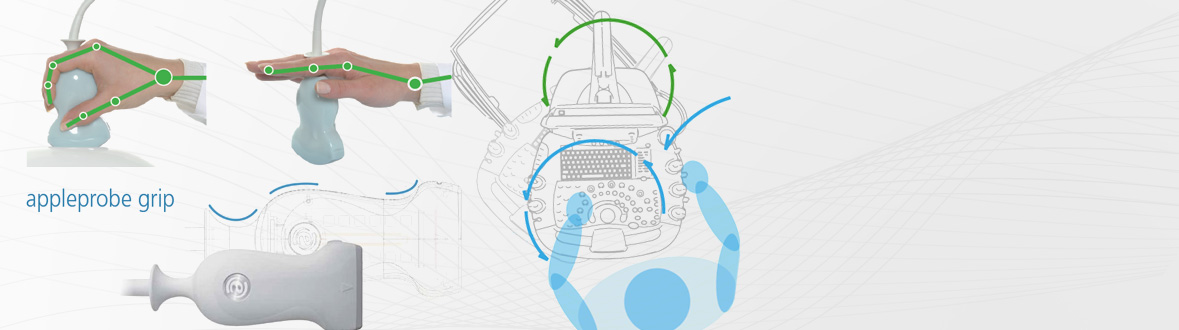
Esaote systems are characterized by a high-definition touch screen which concentrates all the main features of the reconfigurable graphical user interface into a well-defined area close to the trackball, reducing repetitive movements.
Repetitive distant movements were reduced by 40% in abdominal exams and 16% in cardiovascular exams.
A dimensional comparison between the newly introduced Esaote user interfaces and a conventionally designed ultrasound system, showed the following optimizations:
- 25% reduction in the number of controls present on the physical control panel
- 45% reduction in the distance between the trackball and the graphical user controls
- 67% reduction in the distance between the trackball and the function adjustment toggles
- 19% reduction in the distance between the trackball and the TGC sliders
- Trackball 17% closer to the text input system
Esaote appleprobe transducers showed a reduced muscle strength of between 31% and 79%, compared with traditionally-designed transducers, depending on the selected probe (linear or convex) and application (vascular or abdominal).
The reduction in muscular stress required to use the innovative Esaote appleprobe transducers, compared with traditionally designed transducers, represents a valuable and tangible reduction in the possible causes of WRMSD.

Comparison of conventional design and appleprobe design
Take a look at our solutions:
Technology and features are system/configuration dependent. Specifications subject to change without notice. Information might refer to products or modalities not yet approved in all countries. Product images are for illustrative purposes only.. For further details, please contact your Esaote sales representative.



